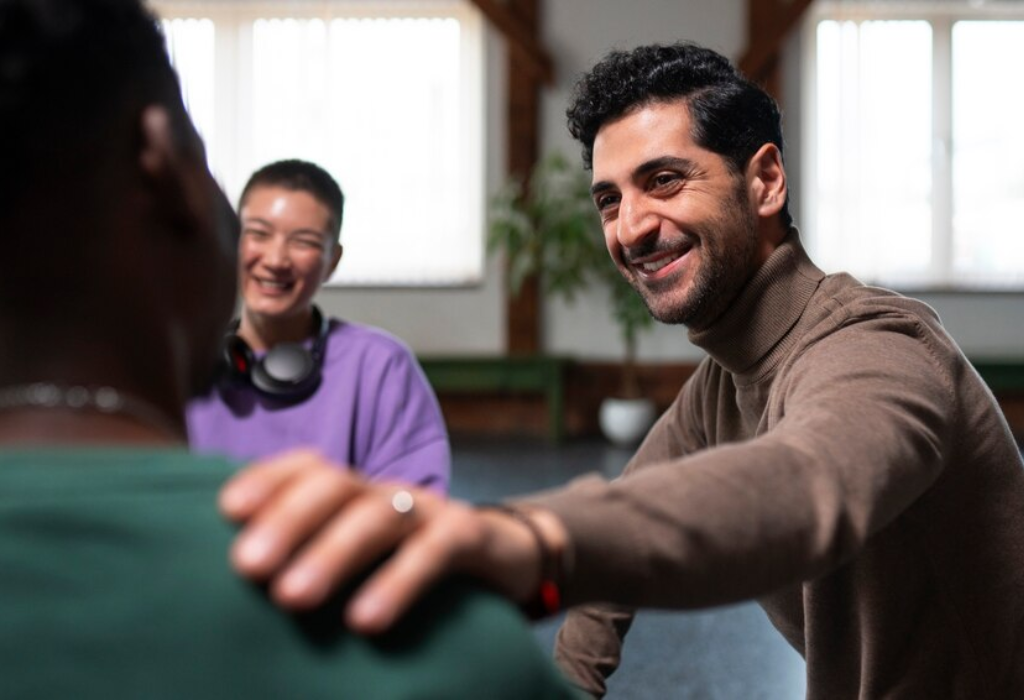
Peers who have walked similar recovery paths bring invaluable insights, empathy, and encouragement to those currently struggling. This shared journey helps build a supportive community, fostering strength and resilience in the face of adversity. Join us as we explore the profound impact of peer connections in the quest for lasting recovery.
What is the purpose of peer support?
Peer support involves the mutual exchange of assistance, encouragement, and understanding between people who share similar experiences or challenges. It is based on the principle of offering support from a place of equality and empathy, rather than a hierarchical or authoritative position. Peers, drawing on their own lived experiences, engage in supportive relationships, providing each other with valuable insights and empathy.
Unique aspects of peer support in recovery
- Non-judgmental and accepting: Peer support offers a stigma-free space for sharing.
- Empathy over expertise: Peers provide understanding based on shared experiences.
- Practical guidance and emotional support: Peers offer both practical advice and emotional assistance.
- Fosters belonging and connection: Peer support reduces isolation, fostering camaraderie among individuals in recovery.
The Many Values of Peer Recovery Support Services
- Solidarity and understanding: Shared experiences foster trust and rapport among peers.
- Relatability and relevance: Peers offer insights and coping strategies based on shared challenges.
- Validation and affirmation: Support from peers who understand instills hope and motivation.
- Sense of community: Peer support creates a supportive network for sharing and mutual assistance.
The Adaptability of Peer Recovery Support Services
Historical background of PRSS
- Origins in mutual aid and self-help movements dating back to the 19th century.
- Early examples include Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA), founded on principles of peer support and mutual assistance.
- Initial grassroots efforts paved the way for formalizing peer recovery support services.
Emergence and growth of peer-led recovery movements
- Rise of peer-led recovery movements in the late 20th century, driven by individuals in recovery advocating for their own support needs.
- Pioneering efforts led to the establishment of peer-run recovery centers, peer support groups, and other community-based initiatives.
- Peer-led organizations such as Faces & Voices of Recovery and the Recovery Advocacy Project played pivotal roles in amplifying the voices of individuals in recovery.
Integration of peer support into mainstream healthcare systems
- Recognition of the value of peer support in promoting recovery outcomes by healthcare professionals and policymakers.
- Inclusion of peer support services in treatment programs, mental health services, and addiction treatment facilities.
- Integration of peer supporters into multidisciplinary healthcare teams, collaborating with clinicians and professionals to provide holistic care.
- Growing acceptance and endorsement of peer recovery support services as an essential component of comprehensive treatment and recovery support systems.
What are the five Principles of Peer Support?
Peer recovery support services embody these core principles to create a nurturing and empowering environment for individuals in recovery.
1. Shared lived experience
- Peers offer support based on their own experiences with addiction and recovery.
- Shared experiences create a sense of understanding and connection among individuals in recovery.
- Personal stories of overcoming challenges inspire hope and provide valuable insights.
2. Mutual respect and empathy
- Peers interact with respect, recognizing each individual’s unique journey and strengths.
- Empathy forms the foundation of peer relationships, fostering trust and rapport.
- Peers offer support without judgment, acknowledging the dignity and worth of every individual.
3. Empowerment and self-determination
- Peer support encourages individuals to take an active role in their recovery journey.
- Peers empower others to set their own goals and make informed decisions about their recovery.
- Through encouragement and guidance, peers foster confidence and self-efficacy.
4. Hope and optimism
- Peer support instills hope by demonstrating that recovery is possible and achievable.
- Peers provide encouragement and reassurance during challenging times, promoting optimism for the future.
- Belief in the potential for positive change fuels motivation and resilience in recovery.
5. Non-judgmental support and acceptance
- Peers offer support without criticism or condemnation, creating a safe and welcoming environment.
- Acceptance of individuals as they are, without expectation or pressure, promotes trust and openness.
- Non-judgmental attitudes encourage honesty and authenticity in peer relationships, facilitating meaningful connections.
By welcoming shared experiences, mutual respect, empowerment, hope, and non-judgmental acceptance, peer supporters play a crucial role in fostering healing, growth, and resilience among their peers. These principles serve as guiding lights, illuminating the path to recovery and offering solace and support to those in need.
Different Recovery Stages and Approaches
Peer support services encompass a wide range of approaches, each tailored to meet the unique needs and preferences of individuals on their recovery journey.
One-on-one peer mentoring
- Individualized support is provided by trained peer mentors based on personal experiences.
- Focus on guidance, encouragement, and goal-setting for individuals in recovery.
Peer-led support groups and mutual aid societies
- Group settings like Alcoholics Anonymous offer platforms for sharing experiences and mutual support.
- Emphasis on self-empowerment and self-management in alternatives like Smart Recovery.
Telephone and online peer support networks
- Accessible helplines and online forums provide support and encouragement remotely.
- Anonymity and convenience allow individuals to seek help at any time and from anywhere.
Peer-run recovery centers and drop-in facilities
- Community-based centers are staffed by individuals with lived experience of recovery.
- Offer a range of services, including support groups, workshops, and recreational activities.
- Provide a welcoming space for informal support and social connections.
Conclusion
Peer Recovery Support Services (PRSS) serve as vital pillars of support and empowerment for individuals navigating the challenges of recovery from substance use disorders and behavioral health issues. Rooted in shared experiences, empathy, and mutual respect, these services offer a beacon of hope and solidarity, fostering healing, growth, and resilience. From one-on-one peer mentoring to group support sessions, and telephone helplines to community-based centers, PRSS provide a diverse array of avenues for individuals to find connection, understanding, and encouragement on their journey to wellness.
If you or someone you know could benefit from peer recovery support services, don’t hesitate to reach out and connect with Bhouses today. Remember, you’re not alone, and there’s strength in seeking support and solidarity. Start your journey to recovery with the empowering embrace of peer support.
FAQs
Que: What is a peer recovery support service?
Ans: Employing a nonmedical framework, social support services are delivered by peer leaders who have firsthand experience with substance use disorder and recovery. These services broaden the spectrum of care by assisting individuals in accessing treatment, offering social support throughout the treatment process, and ensuring continued support post-treatment for a safer transition.
Que: What is the purpose of peer support?
Ans: Through sharing their personal lived experiences and offering practical guidance, peer support workers assist individuals in crafting their own goals, devising strategies for self-empowerment, and actively pursuing steps to construct meaningful and self-directed lives.
Que: What is the difference between a recovery coach and a peer support specialist?
Ans: Recovery coaches, also known as peer specialists, differ from trained counselors, social workers, or mental and behavioral health treatment professionals. While recovery coaches have firsthand experience with addiction or behavioral health issues and are motivated to support others in achieving and sustaining recovery, trained professionals possess specific qualifications and expertise in counseling or mental health treatment.
Que: What is the difference between peer support and therapy?
Ans: Peer support relies on mutual understanding, shared experiences, and peer-to-peer knowledge exchange to foster recovery, empowerment, and social integration. In contrast, therapy is rooted in clinical proficiency, formal training, and evidence-supported interventions.
Que: What are examples of peer support?
Ans: Peer support can take various forms, including in-person meetings or accessing online platforms such as social media networks or dedicated online communities like Mind’s Side by Side. Additionally, individuals may utilize alternative communication methods such as emails, phone calls, or text messages to connect with peer support networks.
Que: What are the duties of a peer support specialist?
Ans: Roles of Peer Support
- Championing individuals in recovery.
- Sharing resources and fostering skill development.
- Cultivating community and nurturing relationships.
- Facilitating recovery groups.
- Mentoring and establishing objectives.
Que: What makes a good peer recovery supporter?
Ans: Relationship-Centered: The connection between the peer worker and the individual receiving support serves as the cornerstone for delivering peer recovery support services. This relationship is characterized by mutual respect, trust, empathy, collaboration, and reciprocity.